Which Of The Following Represents The Size Of Each Component Of Gdp Inã¢â‚¬â€¹ 2014?
Affiliate 19. The Macroeconomic Perspective
19.1 Measuring the Size of the Economy: Gross Domestic Product
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Identify the components of Gross domestic product on the demand side and on the supply side
- Evaluate how gross domestic product (GDP) is measured
- Contrast and calculate GDP, net exports, and net national production
Macroeconomics is an empirical subject, so the showtime stride toward understanding information technology is to measure the economy.
How large is the U.S. economic system? The size of a nation's overall economic system is typically measured by its gross domestic product (Gross domestic product), which is the value of all final goods and services produced within a land in a given year. The measurement of Gdp involves counting up the production of millions of unlike goods and services—smart phones, cars, music downloads, computers, steel, bananas, college educations, and all other new appurtenances and services produced in the electric current year—and summing them into a total dollar value. This task is straightforward: have the quantity of everything produced, multiply information technology past the cost at which each product sold, and add up the total. In 2014, the U.S. GDP totaled $17.4 trillion, the largest GDP in the world.
Each of the market transactions that enter into GDP must involve both a buyer and a seller. The GDP of an economy can exist measured either by the total dollar value of what is purchased in the economy, or past the full dollar value of what is produced. At that place is even a third way, equally we will explicate later.
GDP Measured by Components of Need
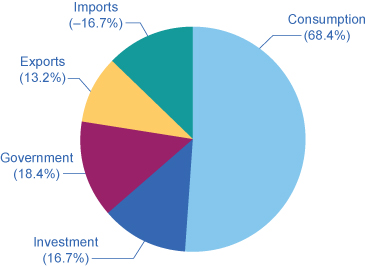
Who buys all of this production? This need can be divided into four main parts: consumer spending (consumption), business spending (investment), government spending on goods and services, and spending on net exports. (See the following Articulate It Up characteristic to understand what is meant by investment.) Table 1 shows how these four components added up to the Gross domestic product in 2014. Effigy 2 (a) shows the levels of consumption, investment, and government purchases over time, expressed as a pct of GDP, while Figure 2 (b) shows the levels of exports and imports equally a percentage of GDP over time. A few patterns almost each of these components are worth noticing. Table i shows the components of GDP from the demand side. Effigy 1 provides a visual of the percentages.
| Components of GDP on the Demand Side (in trillions of dollars) | Percentage of Total | |
|---|---|---|
| Consumption | $eleven.9 | 68.4% |
| Investment | $2.nine | 16.vii% |
| Government | $3.two | xviii.four% |
| Exports | $2.3 | 13.two% |
| Imports | –$2.9 | –sixteen.vii% |
| Total GDP | $17.4 | 100% |
| Table ane. Components of U.South. Gdp in 2014: From the Demand Side. (Source: http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) | ||
What is meant past the discussion "investment"?
What do economists mean by investment, or concern spending? In calculating GDP, investment does not refer to the purchase of stocks and bonds or the trading of fiscal assets. It refers to the purchase of new capital goods, that is, new commercial real estate (such as buildings, factories, and stores) and equipment, residential housing construction, and inventories. Inventories that are produced this year are included in this year's Gross domestic product—fifty-fifty if they have not yet sold. From the auditor's perspective, information technology is as if the firm invested in its own inventories. Business organization investment in 2014 was virtually $three trillion, according to the Bureau of Economic Assay.
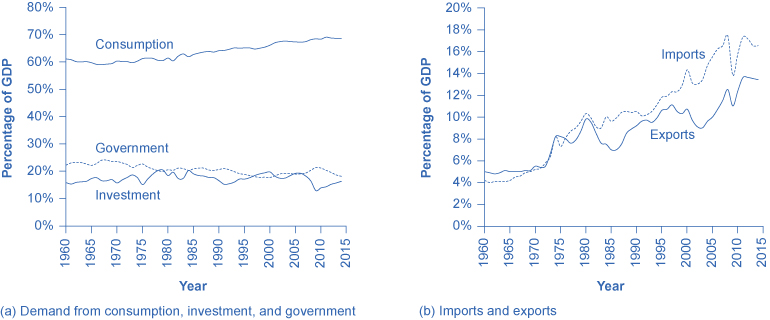
Consumption expenditure past households is the largest component of Gdp, bookkeeping for about 2-thirds of the Gdp in whatever yr. This tells u.s.a. that consumers' spending decisions are a major driver of the economy. However, consumer spending is a gentle elephant: when viewed over time, information technology does non spring around as well much.
Investment expenditure refers to purchases of concrete institute and equipment, primarily past businesses. If Starbucks builds a new store, or Amazon buys robots, these expenditures are counted under business investment. Investment need is far smaller than consumption demand, typically bookkeeping for only almost 15–18% of GDP, but it is very important for the economy because this is where jobs are created. However, it fluctuates more noticeably than consumption. Concern investment is volatile; new applied science or a new product can spur business organization investment, but then confidence can drop and business investment can pull dorsum sharply.
If you lot have noticed any of the infrastructure projects (new bridges, highways, airports) launched during the recession of 2009, you accept seen how important regime spending can be for the economy. Authorities expenditure in the United States is nigh twenty% of GDP, and includes spending by all three levels of government: federal, state, and local. The only part of regime spending counted in need is authorities purchases of appurtenances or services produced in the economic system. Examples include the authorities buying a new fighter jet for the Air Force (federal authorities spending), building a new highway (state authorities spending), or a new school (local authorities spending). A significant portion of government budgets are transfer payments, like unemployment benefits, veteran's benefits, and Social Security payments to retirees. These payments are excluded from Gdp because the government does not receive a new good or service in return or commutation. Instead they are transfers of income from taxpayers to others. If you are curious well-nigh the awesome undertaking of adding up GDP, read the following Clear It Upward characteristic.
How practise statisticians measure GDP?
Government economists at the Bureau of Economic Assay (BEA), inside the U.Due south. Department of Commerce, piece together estimates of GDP from a variety of sources.
Once every v years, in the 2d and seventh year of each decade, the Agency of the Census carries out a detailed census of businesses throughout the United states of america. In between, the Census Agency carries out a monthly survey of retail sales. These figures are adjusted with foreign trade data to account for exports that are produced in the U.s.a. and sold abroad and for imports that are produced abroad and sold here. One time every 10 years, the Census Agency conducts a comprehensive survey of housing and residential finance. Together, these sources provide the principal basis for figuring out what is produced for consumers.
For investment, the Census Bureau carries out a monthly survey of construction and an almanac survey of expenditures on physical capital equipment.
For what is purchased by the federal government, the statisticians rely on the U.S. Section of the Treasury. An annual Census of Governments gathers information on land and local governments. Because a lot of government spending at all levels involves hiring people to provide services, a large portion of authorities spending is also tracked through payroll records nerveless by country governments and by the Social Security Administration.
With regard to foreign trade, the Census Bureau compiles a monthly record of all import and consign documents. Additional surveys cover transportation and travel, and adjustment is fabricated for financial services that are produced in the United states of america for foreign customers.
Many other sources contribute to the estimates of GDP. Information on energy comes from the U.South. Department of Transportation and Department of Energy. Information on healthcare is collected past the Bureau for Health Care Inquiry and Quality. Surveys of landlords find out nearly rental income. The Department of Agriculture collects statistics on farming.
All of these bits and pieces of information go far in dissimilar forms, at different time intervals. The BEA melds them together to produce estimates of GDP on a quarterly basis (every iii months). These numbers are then "annualized" by multiplying by iv. As more information comes in, these estimates are updated and revised. The "accelerate" approximate of GDP for a certain quarter is released one month after a quarter. The "preliminary" approximate comes out i calendar month after that. The "final" estimate is published one month after, simply it is not actually final. In July, roughly updated estimates for the previous calendar year are released. Then, one time every v years, subsequently the results of the latest detailed v-year business census have been processed, the BEA revises all of the past estimates of GDP according to the newest methods and data, going all the way back to 1929.
Visit this website to read FAQs on the BEA site. You tin even email your own questions!

When thinking nigh the demand for domestically produced goods in a global economic system, it is of import to count spending on exports—domestically produced goods that are sold abroad. By the same token, nosotros must also subtract spending on imports—appurtenances produced in other countries that are purchased by residents of this land. The internet export component of GDP is equal to the dollar value of exports (X) minus the dollar value of imports (M), (X – M). The gap between exports and imports is called the trade balance. If a land'due south exports are larger than its imports, then a state is said to have a trade surplus. In the United States, exports typically exceeded imports in the 1960s and 1970s, as shown in Figure 2 (b).
Since the early 1980s, imports have typically exceeded exports, and then the U.s.a. has experienced a trade deficit in near years. Indeed, the trade deficit grew quite big in the belatedly 1990s and in the mid-2000s. Figure 2 (b) as well shows that imports and exports have both risen substantially in contempo decades, fifty-fifty after the declines during the Great Recession between 2008 and 2009. As noted before, if exports and imports are equal, strange merchandise has no effect on total Gross domestic product. Yet, even if exports and imports are balanced overall, foreign trade might nonetheless have powerful effects on detail industries and workers by causing nations to shift workers and physical majuscule investment toward one industry rather than some other.
Based on these 4 components of demand, Gdp can be measured as:
[latex]\begin{array}{r @{{}={}} 50}GDP & Consumption\;+\;Investment\;+\;Government\;+\;Trade\;balance \\[1em] Gdp & C\;+\;I\;+\;M\;+\;(Ten\;-\;M) \cease{assortment}[/latex]
Agreement how to measure out Gross domestic product is important for analyzing connections in the macro economy and for thinking about macroeconomic policy tools.
GDP Measured by What is Produced
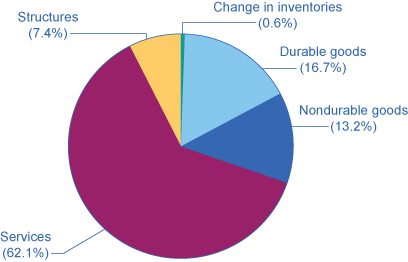
Everything that is purchased must be produced first. Table 2 breaks down what is produced into v categories: durable goods, nondurable goods, services, structures, and the modify in inventories. Before going into detail almost these categories, observe that total GDP measured according to what is produced is exactly the same every bit the GDP measured by looking at the five components of demand. Effigy 3 provides a visual representation of this information.
| Components of Gross domestic product on the Supply Side (in trillions of dollars) | Percentage of Total | |
|---|---|---|
| Goods | ||
| Durable appurtenances | $2.9 | 16.vii% |
| Nondurable appurtenances | $2.3 | 13.ii% |
| Services | $10.eight | 62.1% |
| Structures | $1.3 | 7.4% |
| Change in inventories | $0.1 | 0.6% |
| Full GDP | $17.4 | 100% |
| Table 2. Components of U.S. GDP on the Production Side, 2014. (Source: http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) | ||
Since every marketplace transaction must have both a buyer and a seller, Gdp must exist the same whether measured by what is demanded or by what is produced. Effigy 4 shows these components of what is produced, expressed as a percent of GDP, since 1960.
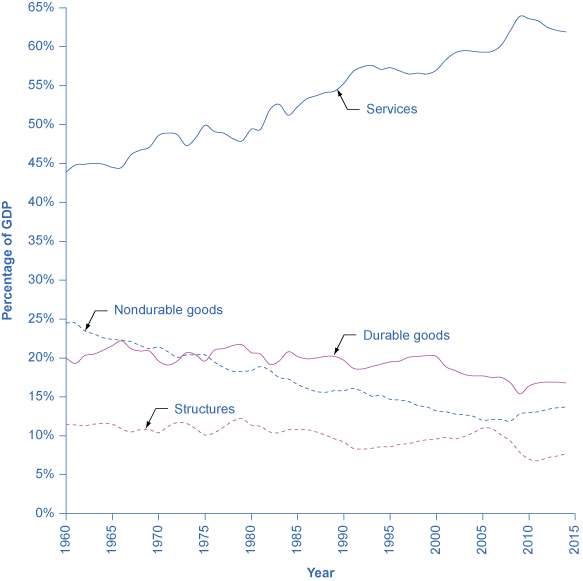
In thinking virtually what is produced in the economic system, many non-economists immediately focus on solid, long-lasting goods, like cars and computers. By far the largest office of GDP, all the same, is services. Moreover, services take been a growing share of Gdp over time. A detailed breakdown of the leading service industries would include healthcare, instruction, and legal and financial services. It has been decades since most of the U.S. economy involved making solid objects. Instead, the almost mutual jobs in a modern economic system involve a worker looking at pieces of newspaper or a estimator screen; meeting with co-workers, customers, or suppliers; or making phone calls.
Even inside the overall category of goods, long-lasting durable goods like cars and refrigerators are almost the same share of the economy as short-lived nondurable goods like food and wearable. The category of structures includes everything from homes, to office buildings, shopping malls, and factories. Inventories is a small category that refers to the goods that have been produced by one business merely accept non yet been sold to consumers, and are still sitting in warehouses and on shelves. The corporeality of inventories sitting on shelves tends to pass up if business organisation is better than expected, or to rising if business concern is worse than expected.
The Trouble of Double Counting
Gdp is divers as the current value of all last goods and services produced in a nation in a year. What are final goods? They are goods at the furthest stage of production at the end of a year. Statisticians who calculate Gdp must avoid the mistake of double counting, in which output is counted more than than once equally it travels through the stages of production. For instance, imagine what would happen if government statisticians showtime counted the value of tires produced by a tire manufacturer, and then counted the value of a new truck sold by an automaker that contains those tires. In this example, the value of the tires would have been counted twice-considering the toll of the truck includes the value of the tires.
To avert this trouble, which would overstate the size of the economy considerably, government statisticians count just the value of final goods and services in the chain of production that are sold for consumption, investment, government, and trade purposes. Intermediate appurtenances, which are goods that get into the production of other goods, are excluded from Gdp calculations. From the example higher up, only the value of the Ford truck will be counted. The value of what businesses provide to other businesses is captured in the final products at the end of the product concatenation.
The concept of Gross domestic product is fairly straightforward: it is but the dollar value of all final goods and services produced in the economic system in a year. In our decentralized, market-oriented economic system, actually calculating the more than $16 trillion-dollar U.S. Gross domestic product—along with how it is changing every few months—is a total-fourth dimension job for a brigade of government statisticians.
| What is Counted in Gdp | What is not included in Gross domestic product |
|---|---|
| Consumption | Intermediate goods |
| Business organization investment | Transfer payments and non-market place activities |
| Government spending on goods and services | Used goods |
| Net exports | Illegal appurtenances |
| Table 3. Counting GDP | |
Discover the items that are not counted into Gdp, as outlined in Table 3. The sales of used appurtenances are not included considering they were produced in a previous yr and are part of that yr'south Gross domestic product. The entire clandestine economy of services paid "nether the table" and illegal sales should exist counted, but is not, considering it is impossible to track these sales. In a recent study by Friedrich Schneider of shadow economies, the hole-and-corner economy in the Usa was estimated to be half-dozen.6% of GDP, or close to $2 trillion dollars in 2013 alone. Transfer payments, such as payment by the authorities to individuals, are not included, because they do not stand for production. Also, production of some goods—such as home production as when you make your breakfast—is not counted because these goods are non sold in the market place.
Visit this website to read about the "New Underground Economy."

Other Ways to Measure the Economy
Besides GDP, in that location are several different merely closely related ways of measuring the size of the economy. We mentioned above that GDP can be thought of as full product and equally full purchases. It tin can also be thought of as total income since annihilation produced and sold produces income.
One of the closest cousins of Gdp is the gross national product (GNP). Gdp includes only what is produced inside a country's borders. GNP adds what is produced by domestic businesses and labor abroad, and subtracts out any payments sent domicile to other countries by foreign labor and businesses located in the U.s.. In other words, GNP is based more than on the production of citizens and firms of a country, wherever they are located, and Gross domestic product is based on what happens within the geographic boundaries of a certain country. For the United States, the gap between Gross domestic product and GNP is relatively small-scale; in recent years, merely about 0.2%. For pocket-sized nations, which may have a substantial share of their population working abroad and sending coin back habitation, the difference can be substantial.
Net national product (NNP) is calculated by taking GNP so subtracting the value of how much physical upper-case letter is worn out, or reduced in value because of crumbling, over the grade of a year. The process by which capital ages and loses value is called depreciation. The NNP can exist further subdivided into national income, which includes all income to businesses and individuals, and personal income, which includes only income to people.
For practical purposes, it is not vital to memorize these definitions. Nonetheless, it is important to exist enlightened that these differences exist and to know what statistic y'all are looking at, then that you do not accidentally compare, say, GDP in one year or for 1 country with GNP or NNP in some other year or some other country. To go an idea of how these calculations work, follow the steps in the following Work It Out feature.
Calculating Gross domestic product, Cyberspace Exports, and NNP
Based on the information in Tabular array 4:
- What is the value of Gross domestic product?
- What is the value of net exports?
- What is the value of NNP?
| Authorities purchases | $120 billion |
| Depreciation | $40 billion |
| Consumption | $400 billion |
| Business Investment | $60 billion |
| Exports | $100 billion |
| Imports | $120 billion |
| Income receipts from rest of the world | $x billion |
| Income payments to residuum of the world | $eight billion |
| Table 4. | |
Step i. To calculate GDP utilize the following formula:
[latex]\begin{array}{r @{{}={}} l}GDP & Consumption\;+\;Investment\;+\;Government\;spending\;+\;(Exports\;-\;Imports) \\[1em] & C\;+\;I\;+\;G\;+\;(Ten\;-\;M) \\[1em] & \$400\;+\;\$60\;+\;\$120\;+\;(\$100\;-\;\$120) \\[1em] & \$560\;billion \end{assortment}[/latex]
Step 2. To summate internet exports, subtract imports from exports.
[latex]\begin{array}{r @{{}={}} l}Net\;exports & Ten\;-\;Grand \\[1em] & \$100\;-\;\$120 \\[1em] & -\$20\;billion \finish{array}[/latex]
Step 3. To summate NNP, utilise the post-obit formula:
[latex]\brainstorm{array}{rcl}NNP & = & GDP\;+\;Income\;receipts\;from\;the\;residual\;of\;the\;world\; \\ & & -\;Income\;payments\;to\;the\;balance\;of\;the\;world\;-\;Depreciation \\[1em] & = & \$560\;+\;\$x\;-\;\$eight\;-\;\$40 \\[1em] & = & \$522\;billion \cease{array}[/latex]
Key Concepts and Summary
The size of a nation's economy is commonly expressed as its gross domestic product (GDP), which measures the value of the output of all goods and services produced inside the country in a year. Gdp is measured by taking the quantities of all goods and services produced, multiplying them by their prices, and summing the total. Since Gross domestic product measures what is bought and sold in the economy, it can be measured either by the sum of what is purchased in the economy or what is produced.
Demand tin be divided into consumption, investment, government, exports, and imports. What is produced in the economic system can exist divided into durable goods, nondurable appurtenances, services, structures, and inventories. To avert double counting, Gross domestic product counts only terminal output of appurtenances and services, not the product of intermediate appurtenances or the value of labor in the chain of production.
Self-Check Questions
- Country A has export sales of $20 billion, government purchases of $1,000 billion, business concern investment is $50 billion, imports are $forty billion, and consumption spending is $2,000 billion. What is the dollar value of Gross domestic product?
- Which of the following are included in GDP, and which are non?
- The cost of hospital stays
- The rise in life expectancy over fourth dimension
- Child care provided by a licensed twenty-four hour period care center
- Child intendance provided by a grandmother
- The auction of a used car
- The sale of a new car
- The greater diverseness of cheese available in supermarkets
- The iron that goes into the steel that goes into a fridge bought by a consumer.
Review Questions
- What are the master components of measuring Gdp with what is demanded?
- What are the main components of measuring Gross domestic product with what is produced?
- Would you ordinarily await GDP as measured by what is demanded to be greater than GDP measured by what is supplied, or the reverse?
- Why must double counting be avoided when measuring GDP?
Critical Thinking Questions
- U.S. macroeconomic data are thought to be among the all-time in the globe. Given what you learned in the Clear Information technology Upward "How exercise statisticians mensurate GDP?", does this surprise yous? Or does this simply reflect the complication of a modernistic economy?
- What does Gdp not tell us nigh the economy?
Problems
Last year, a small nation with abundant forests cut down $200 worth of trees. $100 worth of trees were so turned into $150 worth of lumber. $100 worth of that lumber was used to produce $250 worth of bookshelves. Assuming the country produces no other outputs, and there are no other inputs used in the production of copse, lumber, and bookshelves, what is this nation'south Gross domestic product? In other words, what is the value of the concluding appurtenances produced including copse, lumber and bookshelves?
References
U.S. Section of Commerce: Bureau of Economic Assay. "National data: National Income and Product Accounts Tables." http://bea.gov/iTable/iTable.cfm?ReqID=ix&step=i.
U.South. Department of Commerce: United States Census Agency. "Census of Governments: 2012 Census of Governments." http://www.census.gov/govs/cog/.
United States Department of Transportation. "About DOT." Last modified March 2, 2012. http://www.dot.gov/about.
U.S. Department of Energy. "Energy.gov." http://energy.gov/.
U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. "Agency for Healthcare Enquiry and Quality." http://www.ahrq.gov/.
Usa Department of Agriculture. "USDA." http://www.usda.gov/wps/portal/usda/usdahome.
Schneider, Friedrich. Section of Economics. "Size and Development of the Shadow Economy of 31 European and 5 other OECD Countries from 2003 to 2013: A Further Decline." Johannes Kepler Academy. Last modified April 5, 2013. http://world wide web.econ.jku.at/members/Schneider/files/publications/2013/ShadEcEurope31_Jan2013.pdf.
Glossary
- depreciation
- the process by which capital ages over time and therefore loses its value
- double counting
- a potential mistake to be avoided in measuring Gross domestic product, in which output is counted more than than in one case as information technology travels through the stages of production
- durable good
- long-lasting proficient similar a car or a fridge
- final expert and service
- output used directly for consumption, investment, government, and merchandise purposes; contrast with "intermediate good"
- gross domestic product (GDP)
- the value of the output of all goods and services produced within a country in a year
- gross national product (GNP)
- includes what is produced domestically and what is produced past domestic labor and concern abroad in a year
- intermediate skillful
- output provided to other businesses at an intermediate stage of production, non for final users; dissimilarity with "terminal good and service"
- inventory
- proficient that has been produced, but non however been sold
- national income
- includes all income earned: wages, profits, hire, and turn a profit income
- net national product (NNP)
- GDP minus depreciation
- nondurable practiced
- brusque-lived good like food and wearable
- service
- product which is intangible (in contrast to goods) such as entertainment, healthcare, or education
- construction
- building used as residence, factory, part edifice, retail store, or for other purposes
- merchandise residue
- gap betwixt exports and imports
- trade deficit
- exists when a nation'south imports exceed its exports and is calculated every bit imports –exports
- trade surplus
- exists when a nation's exports exceed its imports and is calculated equally exports – imports
Solutions
Answers to Self-Bank check Questions
- GDP is C + I + K + (X – M). Gdp = $2,000 billion + $50 billion + $1,000 billion + ($20 billion – $40 billion) = $three,030
-
- Infirmary stays are function of Gross domestic product.
- Changes in life expectancy are not market transactions and not office of GDP.
- Child care that is paid for is part of GDP.
- If Grandma gets paid and reports this as income, it is part of Gross domestic product, otherwise non.
- A used motorcar is non produced this twelvemonth, so information technology is not part of Gdp.
- A new automobile is office of Gdp.
- Variety does not count in Gross domestic product, where the cheese could all be cheddar.
- The fe is not counted because it is an intermediate good.
Which Of The Following Represents The Size Of Each Component Of Gdp Inã¢â‚¬â€¹ 2014?,
Source: https://opentextbc.ca/principlesofeconomics/chapter/19-1-measuring-the-size-of-the-economy-gross-domestic-product/
Posted by: devinneymajece1999.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Of The Following Represents The Size Of Each Component Of Gdp Inã¢â‚¬â€¹ 2014?"
Post a Comment